FUNCIONES DEL "SIMPLE PAST"
El "simple past" se utiliza para hablar de una acción que concluyó en un tiempo anterior al actual. La duración no es relevante. El tiempo en que se sitúa la acción puede ser el pasado reciente o un pasado lejano.
EJEMPLOS
- John Cabot sailed to America in 1498.
- My father died last year.
- He lived in Fiji in 1976.
- We crossed the Channel yesterday.
Siempre se utiliza el "simple past" para referirse a cuándo ocurrió algo, de modo que va asociado a ciertas expresiones temporales que indican:
- frecuencia: often, sometimes, always
I sometimes walked home at lunchtime.
I often brought my lunch to school. - un tiempo determinado: last week, when I was a child, yesterday, six weeks ago
We saw a good film last week.
Yesterday, I arrived in Geneva.
She finished her work atseven o'clock
I went to the theatre last night - un tiempo indeterminado: the other day, ages ago, a long time ago People lived in caves a long time ago.
- She played the piano when she was a child.
FUNCIONES DEL "PAST PERFECT"
El "past perfect" hace referencia a un tiempo anterior al pasado reciente. Se emplea para señalar que un evento ocurrió antes que otro en el pasado. No importa cuál de los eventos se mencione primero, porque el tiempo verbal deja claro el orden temporal en que acontecieron.En estos ejemplos, el Evento A es el que primero ocurrió y el Evento B tuvo lugar a continuación, es el más reciente:Evento A Evento B John had gone out when I arrived in the office. Evento A Evento B I had saved my document before the computer crashed. Evento B Evento A When they arrived we had already started cooking. Evento B Evento A He was very tired because he hadn't slept well. FUNCIONES DEL "PAST PROGRESIVE"
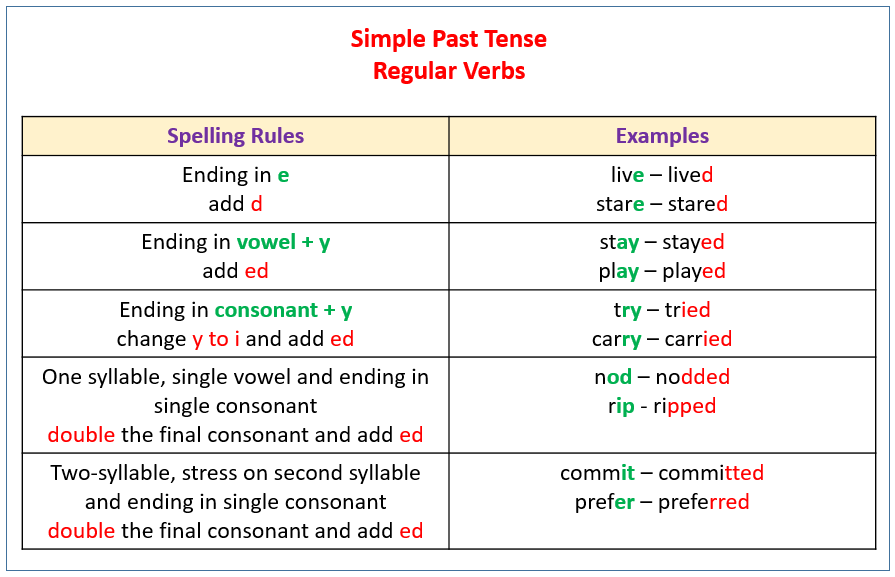
The past progressive puts emphasis on the course of an action in the past.Form
Positive Negative Question I / he / she / it I was speaking. I was not speaking. Was I speaking? you / we / they You were speaking. You were not speaking. Were you speaking? Exceptions in Spelling
Exceptions in spelling when adding ing Example final e is dropped (but: ee is not changed) come – coming
(but: agree – agreeing)after a short, stressed vowel, the final consonant is doubled sit – sitting l as final consonant after a vowel is doubled (in British English) travel – travelling final ie becomes y lie – lying

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario